Visual Brainstorming
Generate, Organize, and Visualize Ideas
Collaborate with the whole team to brainstorm ideas. Let creativity run free while staying focused with visual idea-building techniques.
What is Visual Brainstorming?
Visual brainstorming refers to generating and refining ideas using visualization techniques like mind maps and flowcharts. Whether you're tackling a problem as a group or working on something new solo, visual brainstorming helps you organize ideas and present them clearly.
An online whiteboard is an essential tool for visual brainstorming. It allows for real-time collaboration, keeping everyone engaged and part of the session, no matter if you're together in person or working remotely.
Techniques for Visual Brainstorming
By using a solid framework, you can keep brainstorming sessions structured without limiting your team’s creativity. Which technique suits you best?
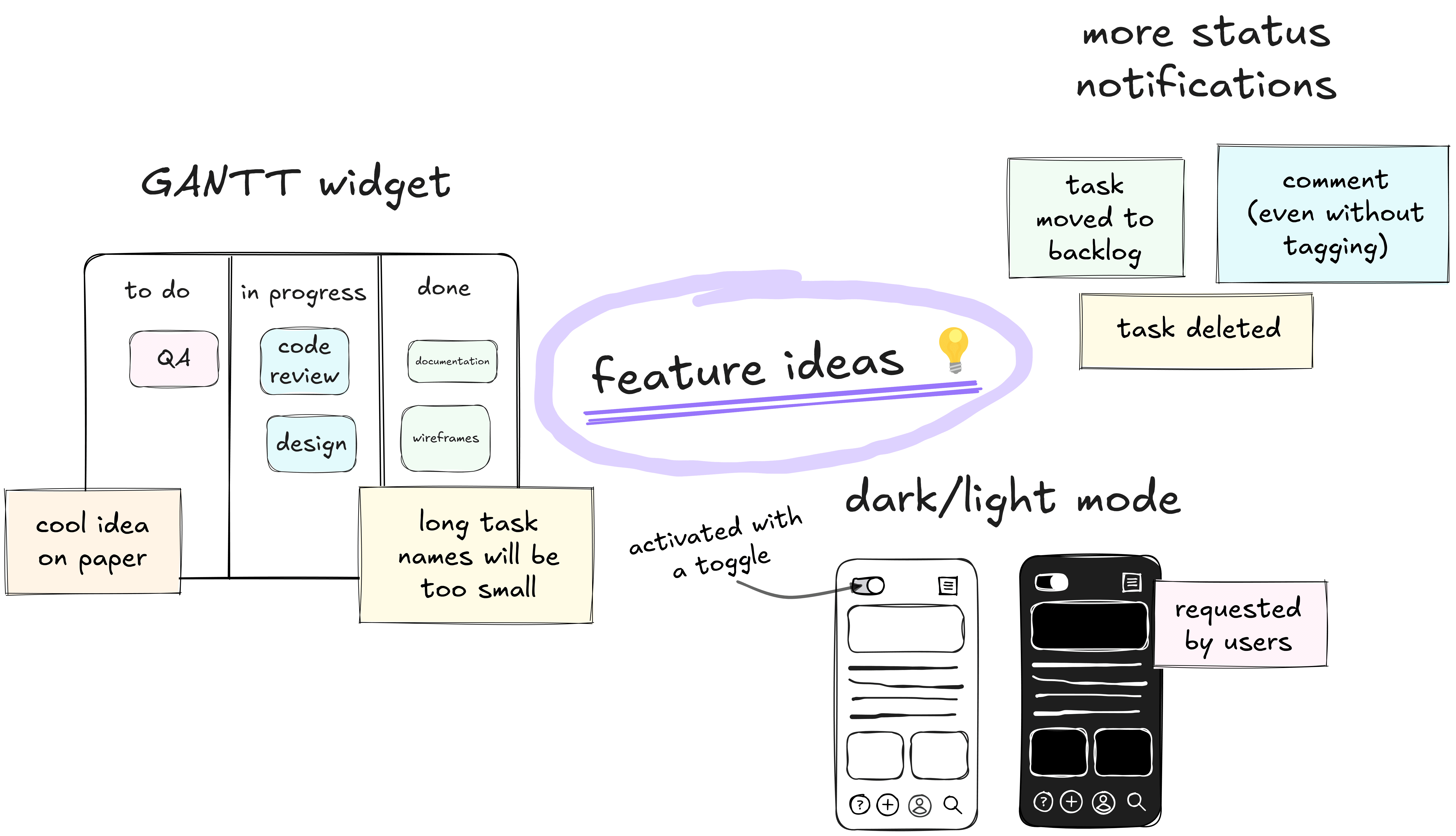
Freewriting and Freedrawing
Set a timer and jot down everything that comes to your mind. Allow ideas to flow freely using either words or sketches without worrying about quality, style, or grammar.
This is an early-stage brainstorming technique that helps break mental blocks. The result will probably be messy, but that's the point: generating spontaneous, unexpected insights that you can refine or discard later.
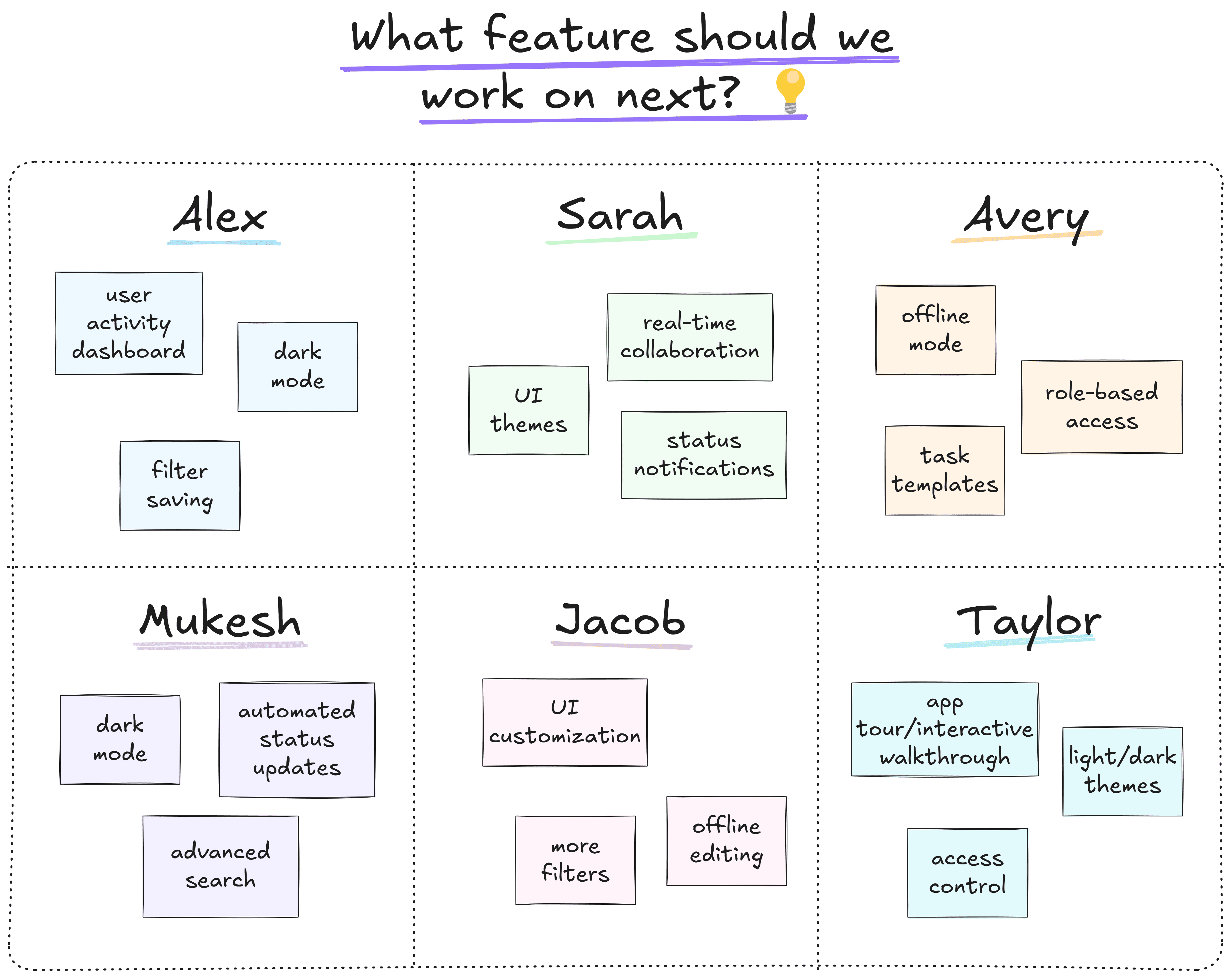
Brainwriting
Ask every team member to note down their ideas individually, to then share and expand them with others. Try the 6-3-5 method: 6 participants writing down 3 ideas each in 5 minutes. Use boxes to jot down ideas, then build on them as a team.
Since everyone has the time to come up with something on their own first, brainwriting is perfect when you want to engage all team members. This helps make sure that every voice is heard and no idea goes unnoticed.

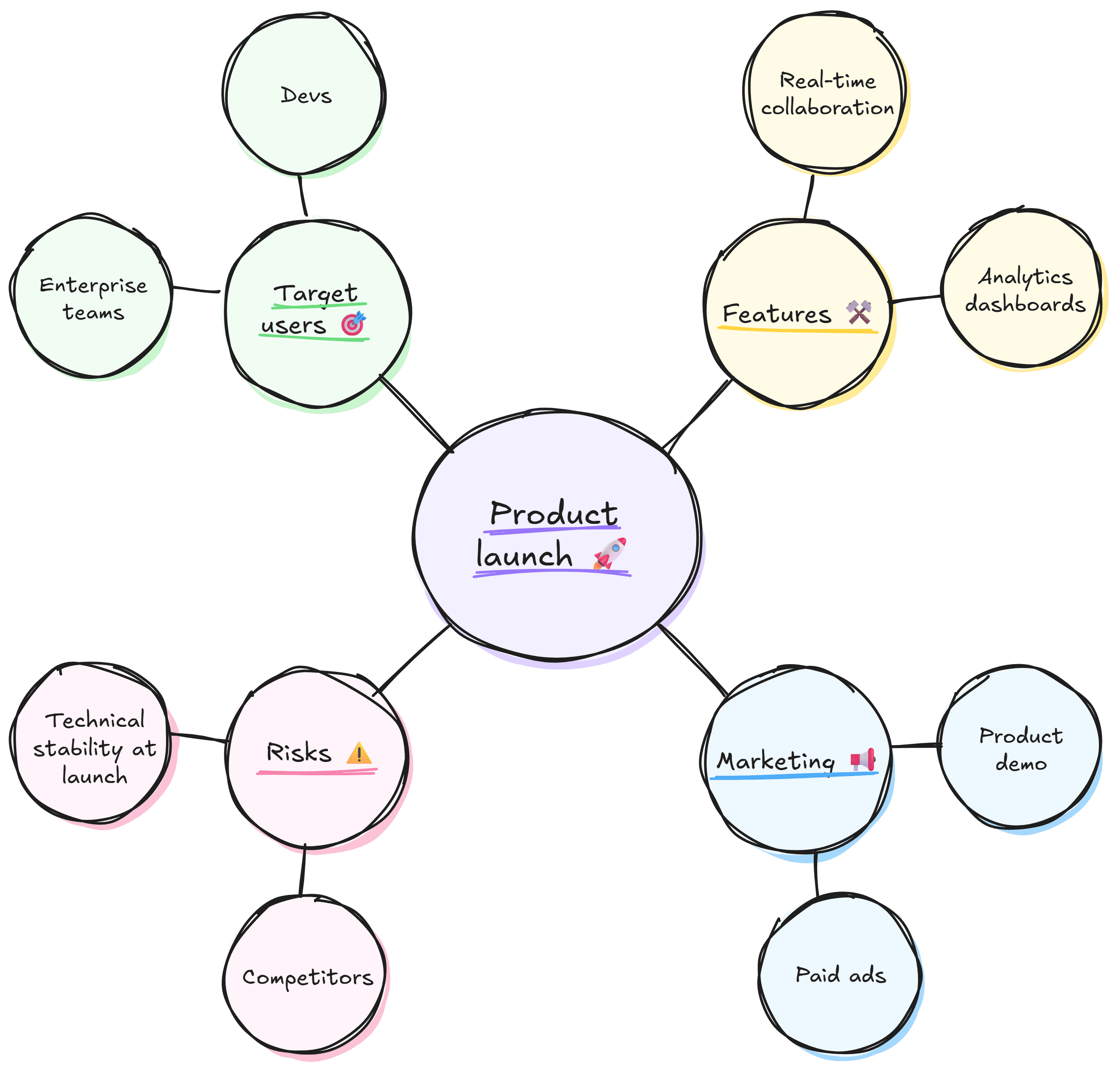
Mind Mapping
Start with a central idea and branch out into related concepts. The visual layout of a mind map makes it easier to spot patterns and uncover gaps in your ideas.
For instance, if your core topic is product launch, create branches for target users, features, marketing, and risks. You can go further, adding sub-branches for related concepts like strategies to reach specific customer groups.
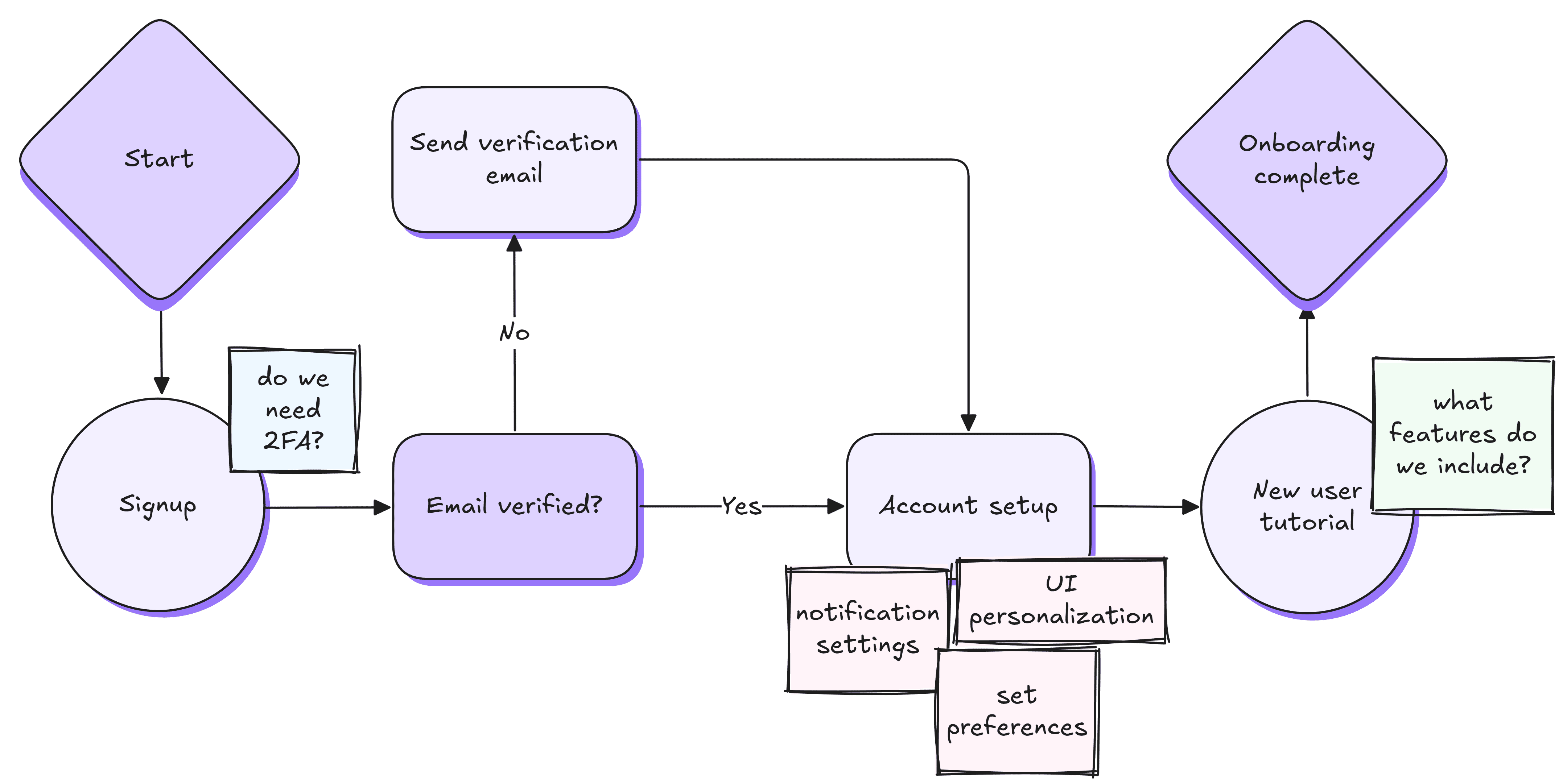
Flowcharts
Break down processes or workflows into sequences of steps. Use arrows and boxes to map out each stage on a flowchart, creating a visual path from start to finish.
Let's say you’re outlining a customer onboarding process. In that case, you can start with signup, then move to account setup, and finish up with a basic tutorial. Seeing all stages laid out helps you find bottlenecks, remove redundancies, and easily brainstorm workflows.
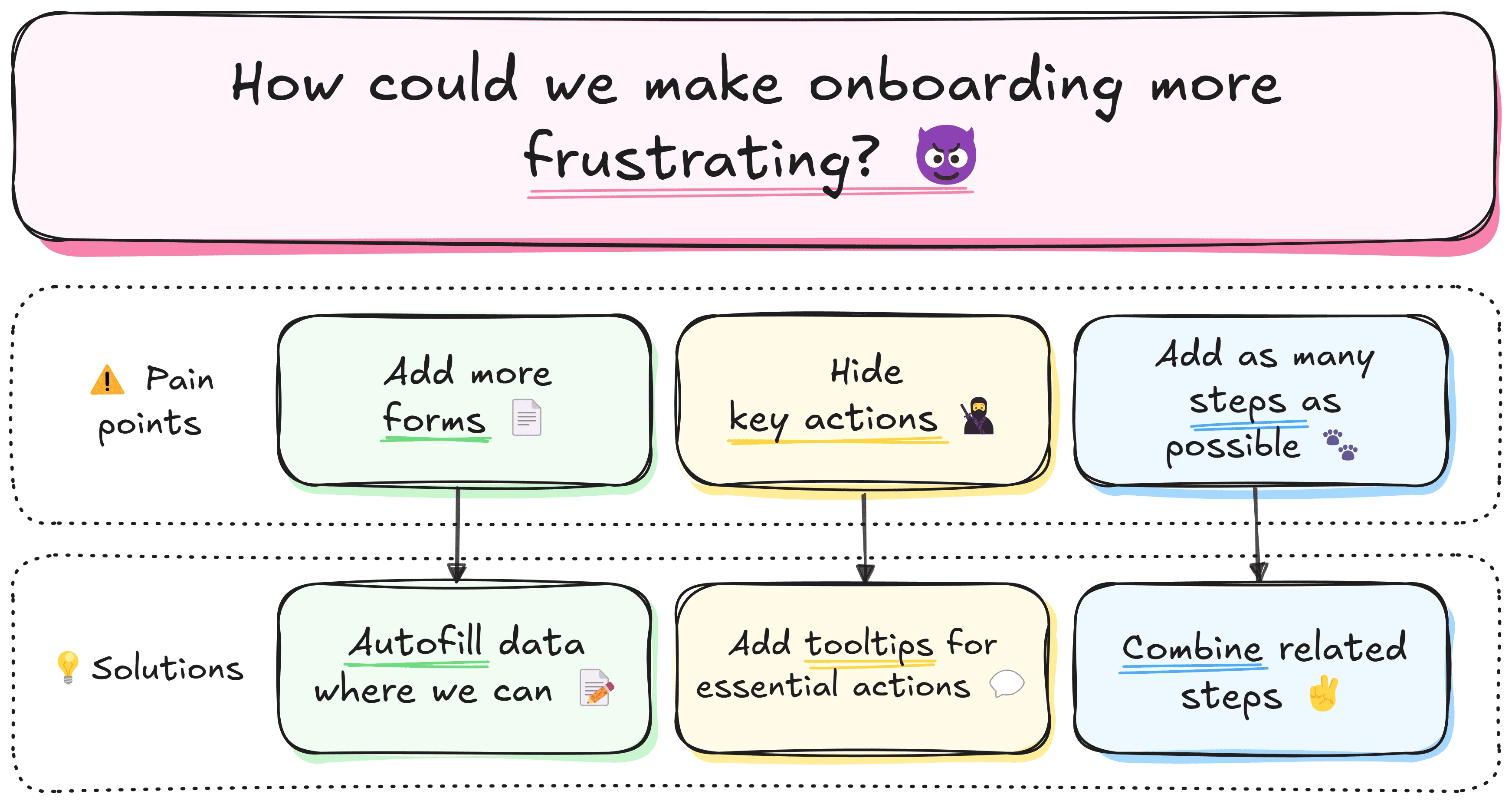
Reverse Brainstorming
Start by asking how to make the problem worse. Then flip each negative into a concrete action you can take to make an improvement. This framework helps you identify the root causes, understand the key pain points to address, or even come up with unexpected solutions.
For instance, if you want to speed up your onboarding flow, ask: “How could we make onboarding more frustrating?” Then, reverse answers like "add extra forms" or "hide key actions" into improvements: auto-filling data or surfacing primary actions.
.png)
SCAMPER Technique
Challenge and improve existing ideas and concepts in seven steps: Substitute, Combine, Adapt or Adjust, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse or Rearrange. Then, create a mindmap with a separate branch for each element to visualize and expand on ideas.
For example, you may decide to substitute the cluttered UI of your product for a more minimal one, magnify the visibility of underused features, or eliminate redundant ones.
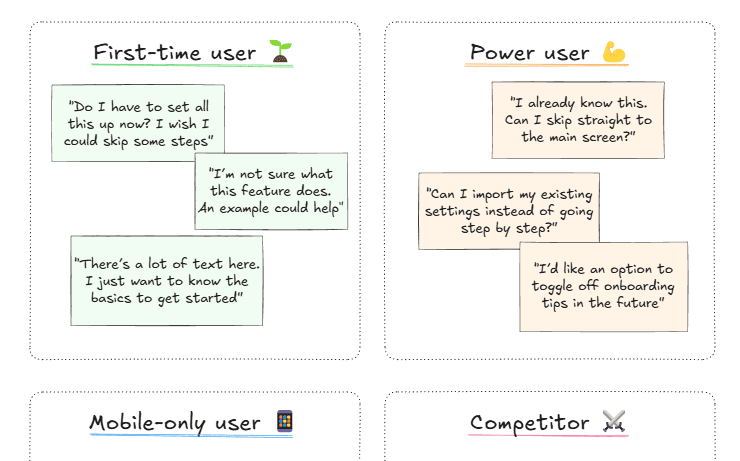
Rolestorming
Adopt different personalities while brainstorming, such as a customer, competitor, or even a fictional character. You can also step into the shoes of your user personas to focus on a specific, well-known audience group. This shift in perspective often uncovers insights you’d miss when thinking only as yourself.
For example, if you’re designing a new onboarding flow, step into the role of a first-time user and note where confusion might arise. Then switch to the persona of a power user to identify opportunities for shortcuts or advanced options.
.png)
The Six Thinking Hats
Take a look at an idea, problem, or concept from six different perspectives: facts (logic), emotions, risks (caution), benefits (optimism), creativity, and process (control). It's a structured approach that ensures well-rounded analysis and considers different points of view and outcomes.
Assign each "hat" to a different person or team. Use color-coded sections for differentiation. For example, when evaluating a new feature rollout, the yellow hat team might highlight user benefits, while the black hats flag potential adoption risks.
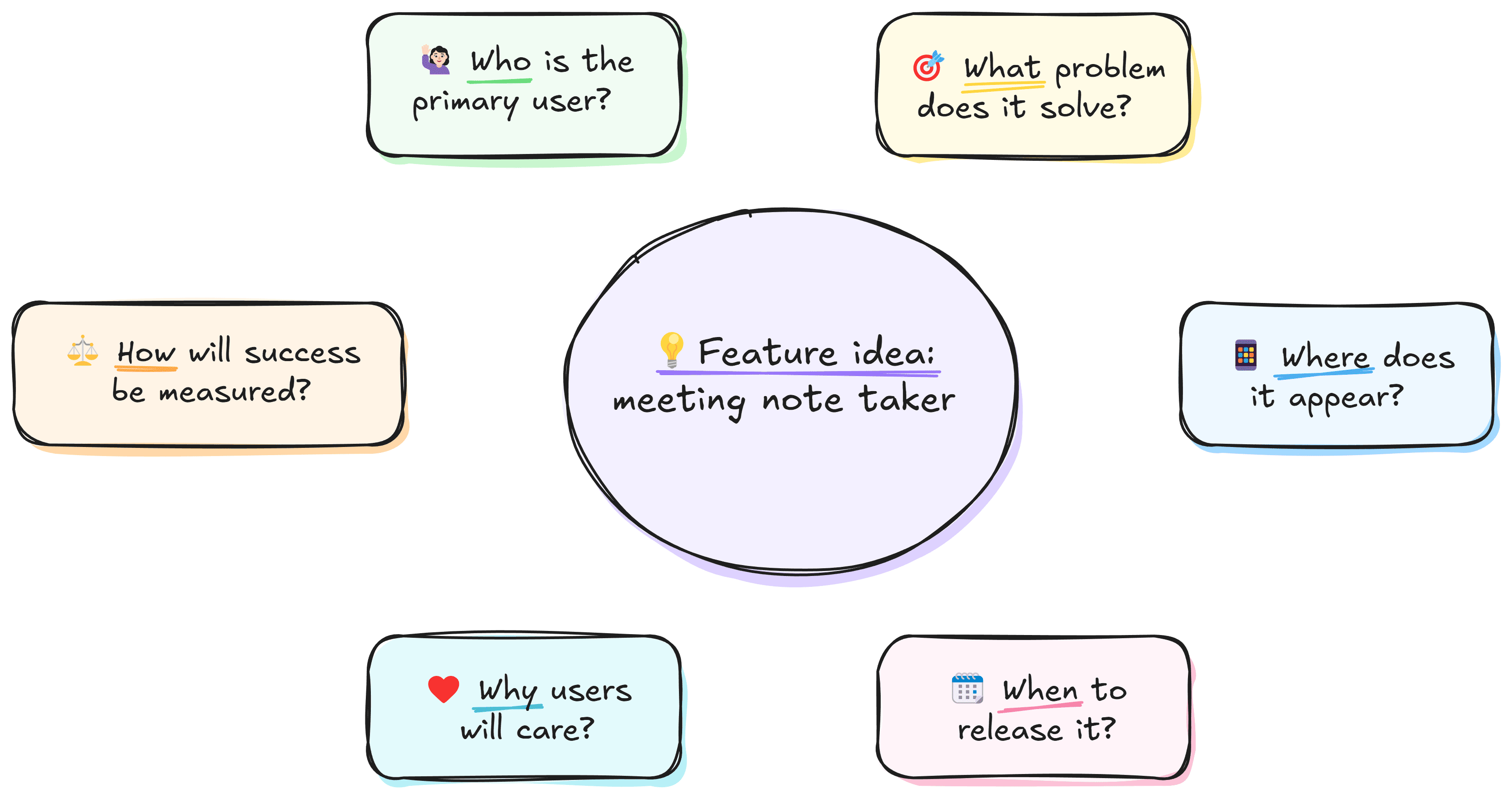
Starbursting
Focus on asking questions first rather than solving problems. Create a central idea and branch out using questions starting with: Who, What, Where, When, Why, and How. This will help you uncover assumptions, clarify requirements, and uncover gaps early.
When launching a new feature, you may ask: Who is the primary user? What problem does it solve? Where will it appear in the product? When should it be introduced? Why will users care? How will success be measured?
.png)
Affinity Diagramming
Organize and consolidate ideas from your brainstorming session into groups based on similarities. This makes your ideas more structured, making them easier to work with, identify gaps, and decide which to prioritize.
For example, if you’re brainstorming features for a new product, cluster ideas into themes like usability, design, and performance. Then, discuss which ones are easy wins and which aren't worth pursuing for now.
How Can Specific Professions Use Visual Brainstorming?
UX/UI Designers
Use mind maps to explore different product features and flowcharts to visualize user flows. Refine existing designs with the SCAMPER technique. Apply rolestorming to create insights into how different users might interact with your product.
Software Developers
Brainstorm technical workflows using flowcharts. Adapt or improve existing features with SCAMPER. Uncover potential issues in development through reverse brainstorming and create affinity diagrams to group related technical problems.
Marketers
Quickly generate campaign ideas with brainwriting. Use starbursting to develop marketing strategies by answering key questions, Identify potential pitfalls and challenges through reverse brainstorming.
Project Managers
Evaluate a project’s risks, benefits, and emotional impact on the team using the six thinking hats framework. Consider stakeholders’ perspectives through rolestorming. Visualize project timelines and dependencies with mind maps.
Tips and Tricks for Visual Brainstorming
Best Practices for Visual Brainstorming
- Use time limits: Set time limits for each technique or round. This ensures that ideas flow quickly and prevents the session from dragging on or becoming repetitive.
- Mix techniques: Don’t stick to just one method. Use techniques like SCAMPER and mind mapping together to explore different aspects of a problem and create a more comprehensive set of ideas.
- Assign a facilitator: Pick one person who'll keep the session on track, ensuring techniques are followed, time limits are adhered to, and the discussion stays focused.
- Follow up on ideas: After the session, review the ideas, organize them into actionable tasks, and assign responsibilities for next steps.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Lack of Focus: Failing to set a clear objective can lead to a scattered session where no concrete ideas emerge. Always define the problem or goal first.
- Neglecting individual thinking: Encourage individual contributions before discussing ideas as a group to avoid conforming to one person’s opinions or ideas.
- Overloading with ideas: Generating too many ideas without narrowing them down can result in a lack of actionable solutions. Make sure to prioritize ideas based on relevance and feasibility.
How to Brainstorm in Excalidraw
- Organize ideas visually: Use color-coding, shapes, and arrows to group related ideas, create connections, and highlight key concepts.
- Add context: Link to objects, other scenes, or external sources using the Cmd/Ctrl+K shortcut.
- Build flowcharts in seconds: Press R or 2 to create a rectangle. Change its shape with Tab. With the object selected, press Cmd/Ctrl+Arrow to create a node. Use the shortcut multiple times to create additional nodes.
- Export for follow-up: After the session, export the board as an image or share it as a link for future reference. This ensures that no ideas are lost and can be reviewed or developed later.
Wrapping Up
Visual brainstorming is a simple and effective way to come up with ideas and spot problems. Diagrams, charts, and freehand drawings allow you to turn abstract thoughts into tangible ideas that are easy to understand for anyone in your team.
Using a brainstorming framework helps you and your team stay creative without losing focus. When combined, these techniques can take you all the way from freeflowing inspiration to actionable ideas.
Business Use or Teamwork? Try PLUS Features
💬 Comments: Allow the whole team to share their ideas, join the discussion, and keep the conversation organized.
🎙️ Voice hangouts and screenshare: Invite your team to a live brainstorming session without the need for additional tools.
📺 Presentations: Turn ideas into slides in a few clicks to easily share them or present live.
📂 Work organization: Use scene collections, user accounts, access controls, and team workspaces to keep inspiration neat and manageable.



